Air to Fuel Ratio in a Diesel YouTube

This is also known as the air/fuel ratio, or AFR for short. By 'a bit rich' we mean there is too much fuel being fed into the engine, and by 'a bit lean' we mean there is not enough fuel, therefore the air/fuel ratio is incorrect and needs adjusting to get the balance right again. When talking about air/fuel ratios you will also hear.
Air Fuel ratio Stoichiometric air fuel ratio IC ENGINE YouTube

Currently, there is a lack of research that has conducted a comparative analysis regarding the impact of air-fuel ratio on the performance of diesel fuel blended with Hydrogen and FAME. This research article examines three fuel blends to determine four critical diesel engine parameters (BTE, Brake Torque, NO x concentration, and BMEP) at five.
PPT OBJECTIVES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4431556
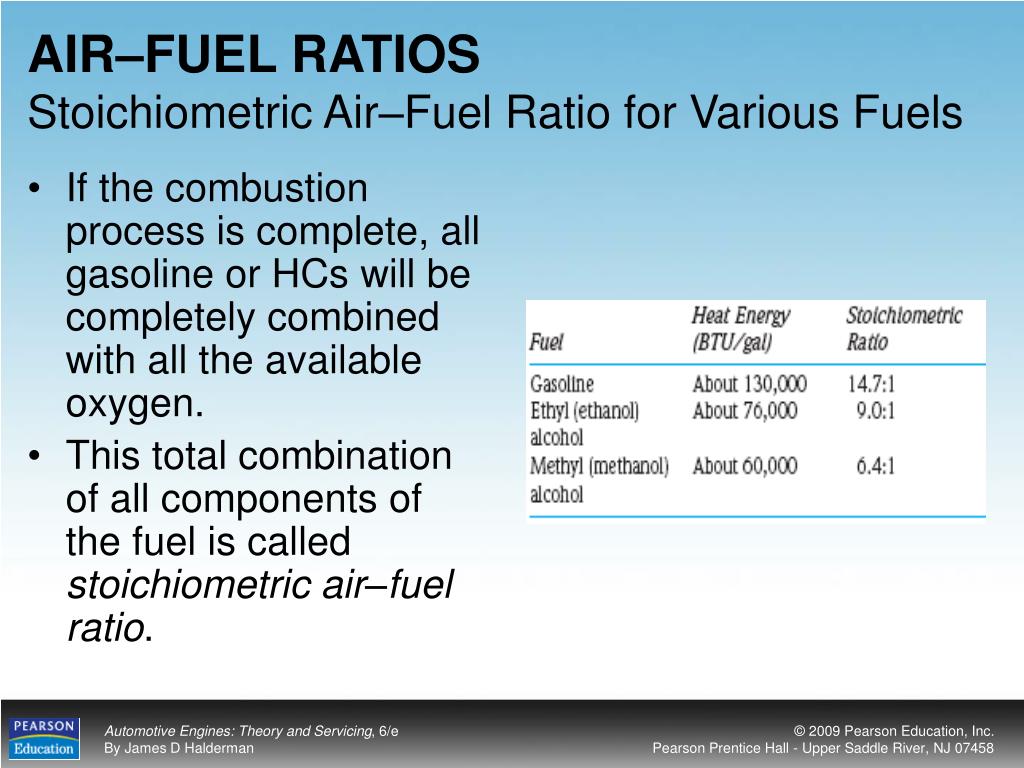
A non-turbo diesel, such as a Toyota Coaster with 1HZ engine, would generally be tuned in between 15-16:1. This means it is running just on the clean side of exhaust emissions. Any lower in AFR and it may begin to smoke. An aftermarket turbocharged diesel, such as a Toyota LC100 with 1HZ engine, would be best running at around 19-20:1 AFR or.
Airfuel ratio for CNGHydrogenDiesel with air. Download Scientific Diagram

Remember that a stoichiometric equivalence factor (λ = 1.00) means an air fuel ratio of 14.7:1 for gasoline engines and 14.5:1 for diesel engines. Go back. Air fuel ratio and engine performance. The engine performance in terms of power and fuel consumption is highly dependent on the air fuel ratio.
NOx Storage and Reduction for Diesel Engine Exhaust Aftertreatment IntechOpen

Air-fuel equivalence ratio, λ (lambda), is the ratio of actual AFR to stoichiometry for a given mixture. λ = 1.0 is at stoichiometry, rich mixtures λ < 1.0, and lean mixtures λ > 1.0. There is a direct relationship between λ and AFR. To calculate AFR from a given λ, multiply the measured λ by the stoichiometric AFR for that fuel.
How to Decide Perfect AirFuel Ratio in IC Engine? YouTube

The air-fuel ratio (AFR) of a diesel engine is typically higher than that of a petrol engine. Diesel engines operate on a leaner combustion process, where the AFR can range from 18:1 to 70:1 by mass or higher. The specific AFR for a diesel engine can vary depending on factors such as engine design, load, and speed.
Comparison of the (air/fuel) ratio. Download Scientific Diagram

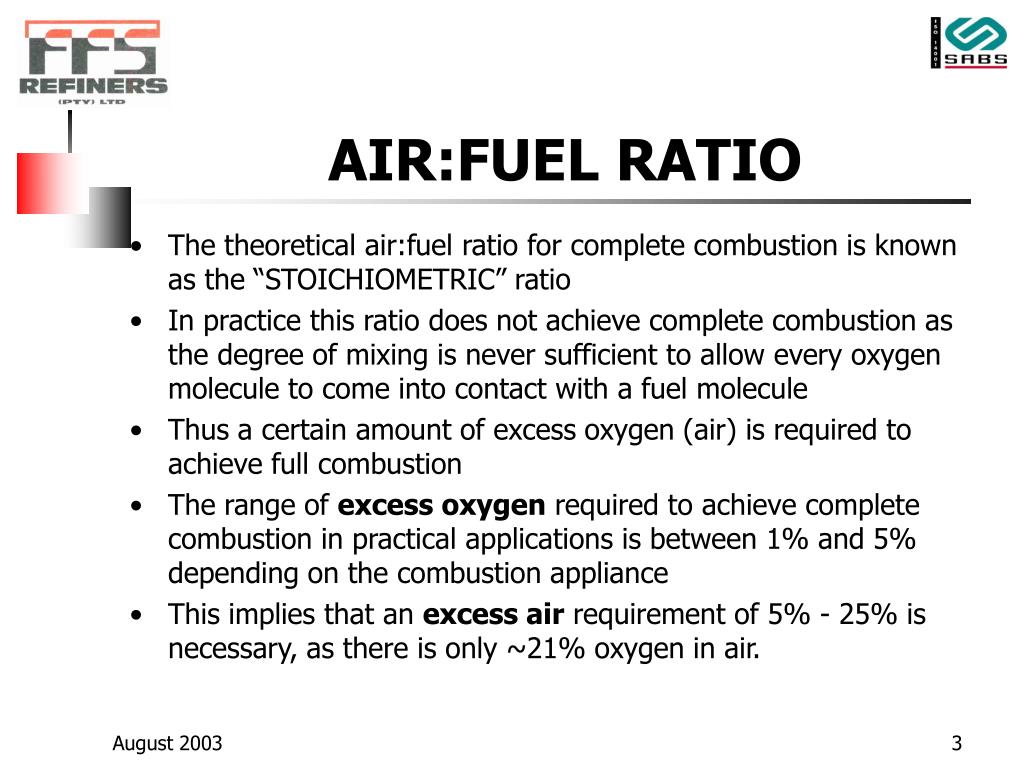
The Diesel Engine. • Intake air not throttled - Load controlled by the amount of fuel injected >A/F ratio: idle ~ 80 >Full load ~19 (less than overall stoichiometric) • No "end-gas"; avoid the knock problem - High compression ratio: better efficiency • Combustion: - Turbulent diffusion flame - Overall lean.
How to Optimize the Fuel / Air Ratio on a Reheat Furnace

As a general guideline we'll normally want to keep the air fuel ratio leaner than approximately lambda 1.1 to 1.2 or 15.9:1 through to 17.4:1 on the air fuel ratio scale under full power operation in order to control exhaust smoke and combustion temperature. 02:54. One of the unique aspects of tuning a turbocharged diesel engine is that we can.
Air Fuel Ratio Gauge Narrow Band 52mm Muscle Black SAAS Automotive

Air-fuel ratio numbers higher than stoichiometric mixture are considered lean air-fuel mixtures, which are more efficient but cause damages to the engine and generate higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) emission.. (2015) Methodologies for air-fuel ratio and trapped mass estimation in diesel engines using the in-cylinder pressure.
Airfuelratio for exhaust SI gasoline emission Download Scientific Diagram

Methodologies for Air-Fuel ratio and trapped mass estimation in Diesel engines using the in-cylinder pressure measurement, Energy Procedia S1876-6102(15)02610-7. [10] Arsie I., Pianese C., Sorrentino M. (2010).
PPT COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1226820
In this episode of Diesel Insights, DT's Nick Priegnitz goes into detail about the importance of a diesel engine's air-to-fuel ratio, especially in tuned tru.
PPT Internal Combustion Engines PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3502358

The stoichiometric ratio or ideal air-fuel mixture for a gasoline engine is 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel, but this can vary. A rich air-fuel mixture contains less air than the stoichiometric ratio, whereas a lean mixture contains more air. You can use a scan tool to check the fuel trim data and determine if the engine is running rich or lean.
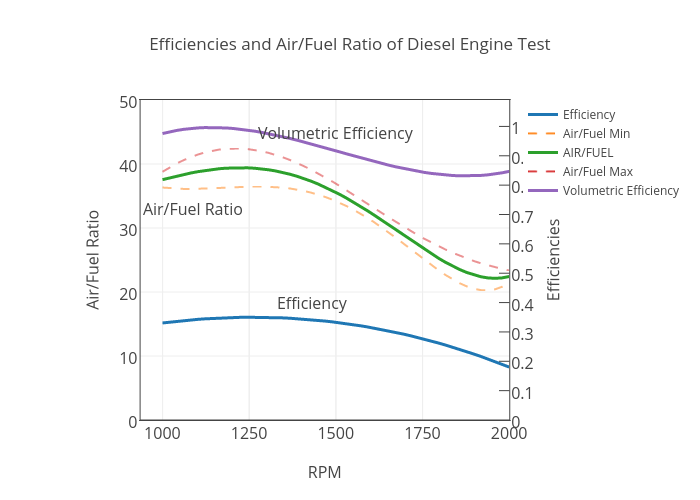
Efficiencies and Air/Fuel Ratio of Diesel Engine Test scatter chart made by plotly
With a turbo diesel, it begins to smoke/soot at an air-fuel ratio of 16-15:1. In order for a turbo diesel to control its exhaust gas temperatures (EGTs) it needs to run lean, where a turbo gasoline vehicle needs to run slightly richer in higher RPM and under higher loads to quench EGT's to run cooler, protect the turbo and prevent knock.
Innovate LM2 Dual "BASIC" Digital Air/Fuel Ratio Wideband Meter (2 O2 Sensor)

In addition, stoichiometric air-to-fuel ratio allows usage of three-way catalyst (TWC), which is capable of reducing carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC),. Diesel fuel consists mainly of paraffins, aromatics and naphthenes. The hydrocarbons of gasoline contain typically 4-12 carbon atoms with boiling range between 30 and 210 °C, whereas.
Air Fuel Ratio Explained YouTube
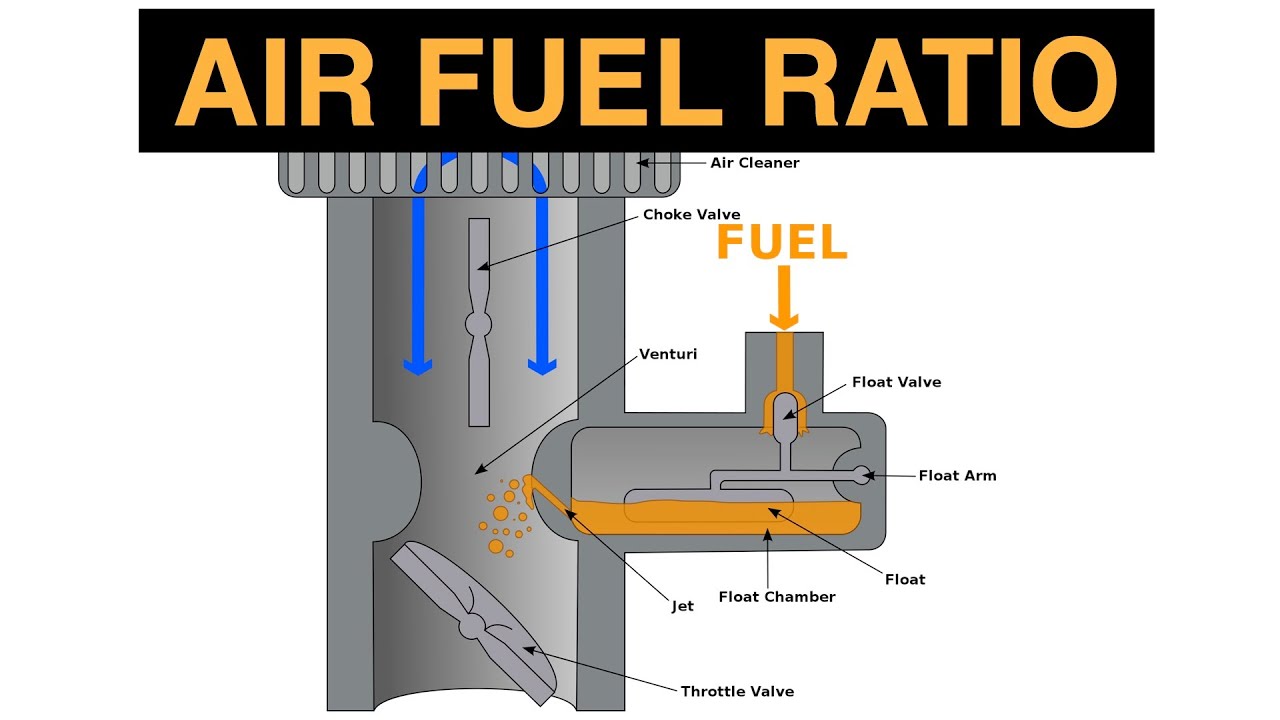
The stoichiometric air-fuel ratio is the ideal ratio at which complete combustion of the fuel occurs, and there is neither excess oxygen nor unburned fuel. For gasoline, the stoichiometric AFR is approximately 14.7:1 (by mass), meaning 14.7 units of air for every unit of fuel.
426 Hemi Build Size Does Matter, Part 1 Hot Rod Network

4.1.3 The characteristics of engine air-fuel ratio and exhaust gas recirculation rate. Engine air-fuel ratio is defined as the mass flow rate ratio of fresh air to fuel. The shape of the air-fuel ratio contours is largely affected by the type of turbocharger and EGR rate. An excessively high air-fuel ratio may produce high pumping loss.