PPT FIXED AND RANDOM EFFECTS IN HLM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6594908

There are two popular statistical models for meta-analysis, the fixed-effect model and the random-effects model. The fact that these two models employ similar sets of formulas to compute statistics, and sometimes yield similar estimates for the various parameters, may lead people to believe that the models are interchangeable.
Choosing Among Pooled OLS, Random Effect and Fixed Effect Model Download Scientific Diagram

probably fixed effects and random effects models. Population-Averaged Models and Mixed Effects models are also sometime used. In this handout we will focus on the major differences between fixed effects and random effects models. Several considerations will affect the choice between a fixed effects and a random effects model. 1.
Figure B 1 Fixedand mixedeffects models fit to simulated data with... Download Scientific

Random Effects. The opposite of fixed effects are random effects. These variables are—like the name suggests—random and unpredictable; they are literally random effects. Examples: The price for a three-course-dinner varies wildly depending on location (e.g. Yulee, Florida will be a lot cheaper than New York City).
Fixed effects and Random effects model ln (MarketShare) Download Table

This article challenges Fixed Effects (FE) modelling as the 'default' for time-series-cross- sectional and panel data. Understanding differences between within- and between-effects is crucial when choosing modelling strategies. The downside of Random Effects (RE) modelling - correlated lower-level covariates and higher-level residuals.
Fixed Effect vs. Random Effects Models Common Mistakes in MetaAnalysis and How To Avoid Them

In statistics, a fixed effects model is a statistical model in which the model parameters are fixed or non-random quantities. This is in contrast to random effects models and mixed models in which all or some of the model parameters are random variables. In many applications including econometrics and biostatistics a fixed effects model refers to a regression model in which the group means are.
PPT Fixed Effects Estimation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID246255

Abstract. There are two popular statistical models for meta-analysis, the fixed-effect model and the random-effects model. The fact that these two models employ similar sets of formulas to compute statistics, and sometimes yield similar estimates for the various parameters, may lead people to believe that the models are interchangeable.
ECON 407 Fixed Effects for Panel Data Rob Hicks

Fixed-effects and random-effects models are the most commonly employed statistical models for meta-analysis. In Table 4, we provide a concise summary of comparative characteristics of the fixed-effects and random-effects model. In Fig. 1, we provide a decision flow chart for the selection of the statistical model for meta-analysis.
Fixedeffect versus randomeffects model in metaregression analysis Pocket Dentistry

Random effects and fixed effects are two important concepts in statistical modeling. They refer to the variability in the data that is not explained by the model, while they are the parameters that are estimated in the model and assumed to be constant across all levels of the factor. Both effects have their own advantages and disadvantages.
PPT Fixed vs. Random Effects PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2984955
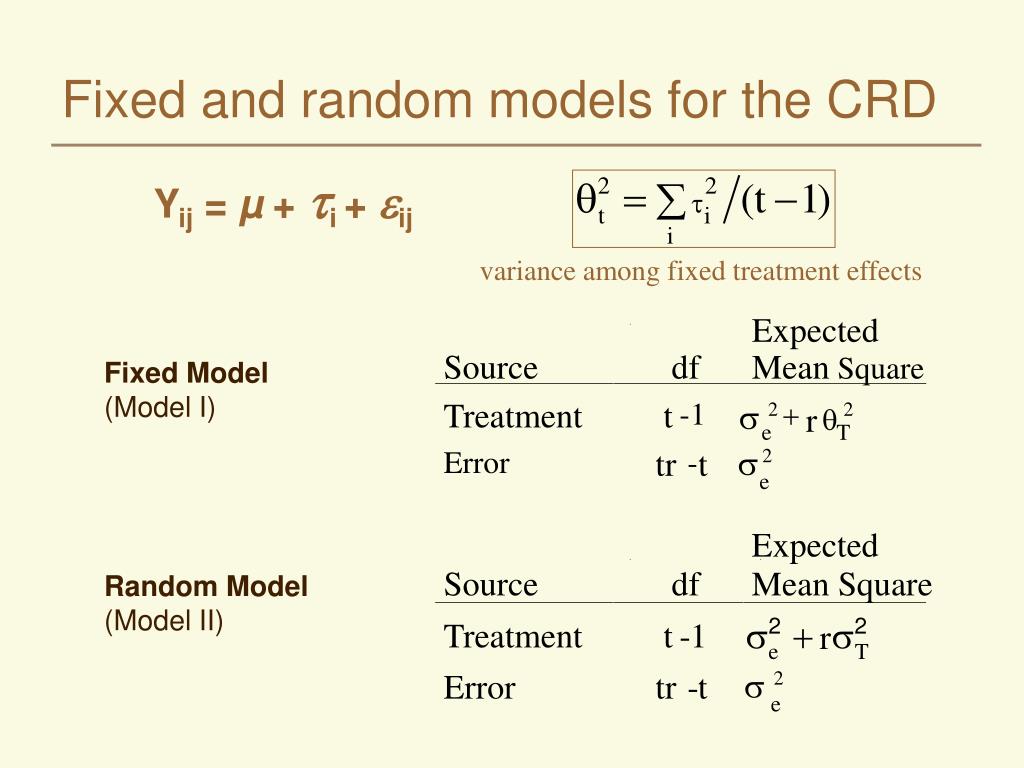
both fixed and random effects are called "mixed models" or "mixed effects models" which is one of the terms given to multilevel models. Fixed and Random Coefficients in Multilevel Regression(MLR) The random vs. fixed terminology is commonly used in multilevel modeling. 2. The . intercepts and slopes
Choosing FixedEffects, RandomEffects or Pooled OLS Models in Panel Data Analysis using Stata

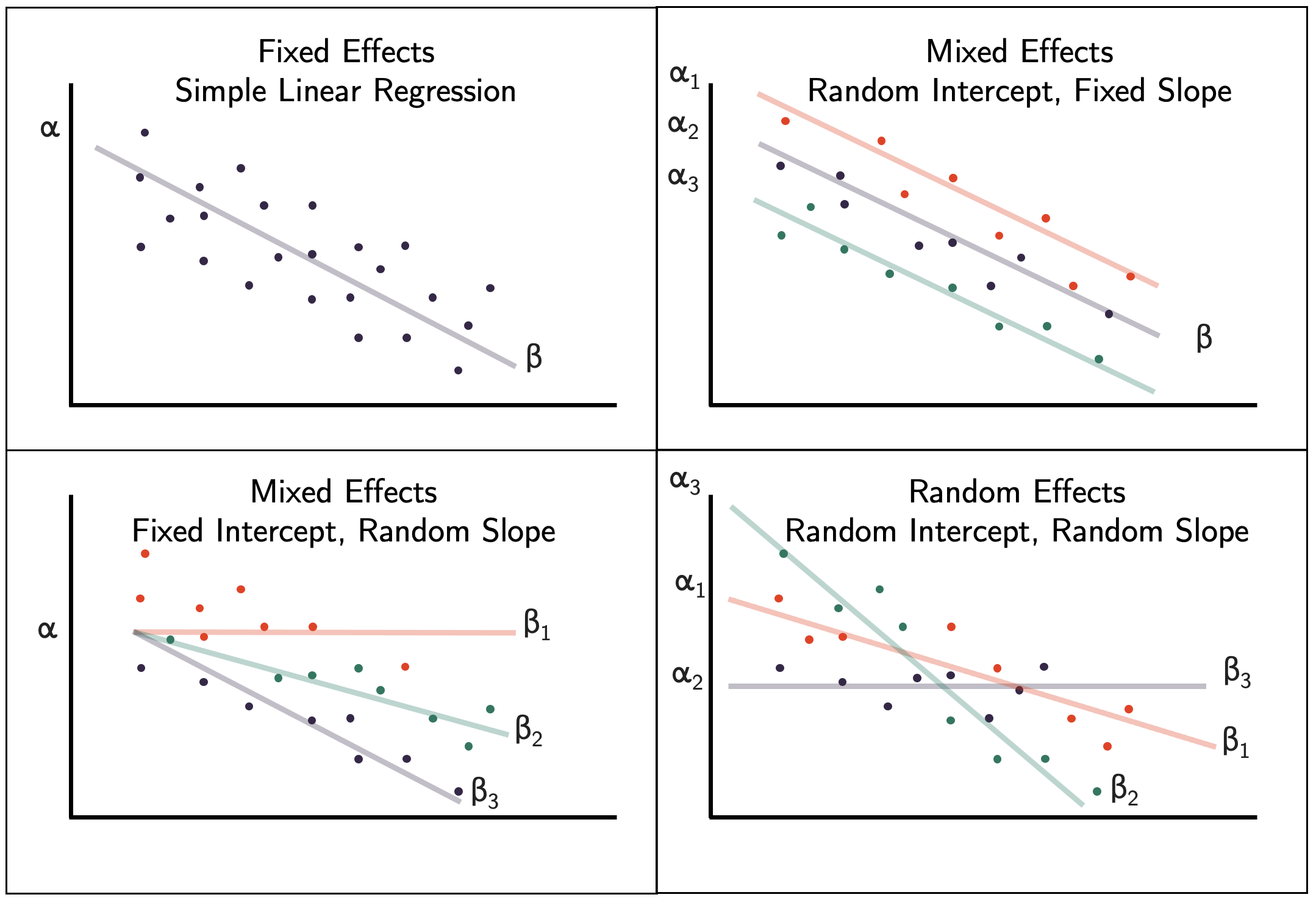
A mixed effects model is a type of regression model that combines both fixed and random effects. Mixed effects models are useful when there is variation in the effect of a factor across groups or individuals, but some of the variation is systematic (i.e., can be explained by specific variables) and some is random (i.e., cannot be explained by.
Fixed and Random Factors (Module 2 8 2) YouTube

In the fixed-effect model, we concluded the observed effect size was the sum of the true effect size and a random sampling error: Ti = θ + εi where \ ( {\varepsilon}_i\sim N\left (0, {\sigma}_i^2\right) \). We can use Fig. 4 to derive the new equations describing the relationship between observed and true effects.
Chapter 6 Fixed or random effects An Introduction to R, LaTeX, and Statistical Inference
Second, the estimate of the effect size differs between the 2 models. In this case, the random-effects model results in a larger effect size, 2.39 vs 2.11 for the fixed-effect model. The results generated from fixed-effect and random-effects models can be the same or different, with either model yielding a higher estimate of the effect size.
Different regression models with Panel data (fixedeffects, randomeffects, and pooled OLS)

Comparing the effects of battery brand as a fixed vs. a random effect, depending on the study design. Includes a worked example for using R to model a single random effect for the battery data. 6.3: Random Effects in Factorial and Nested Designs EMS formulas and F-tests for factorial vs nested designs, in two-factor studies.
Fixed Effects and Random Effects Models YouTube
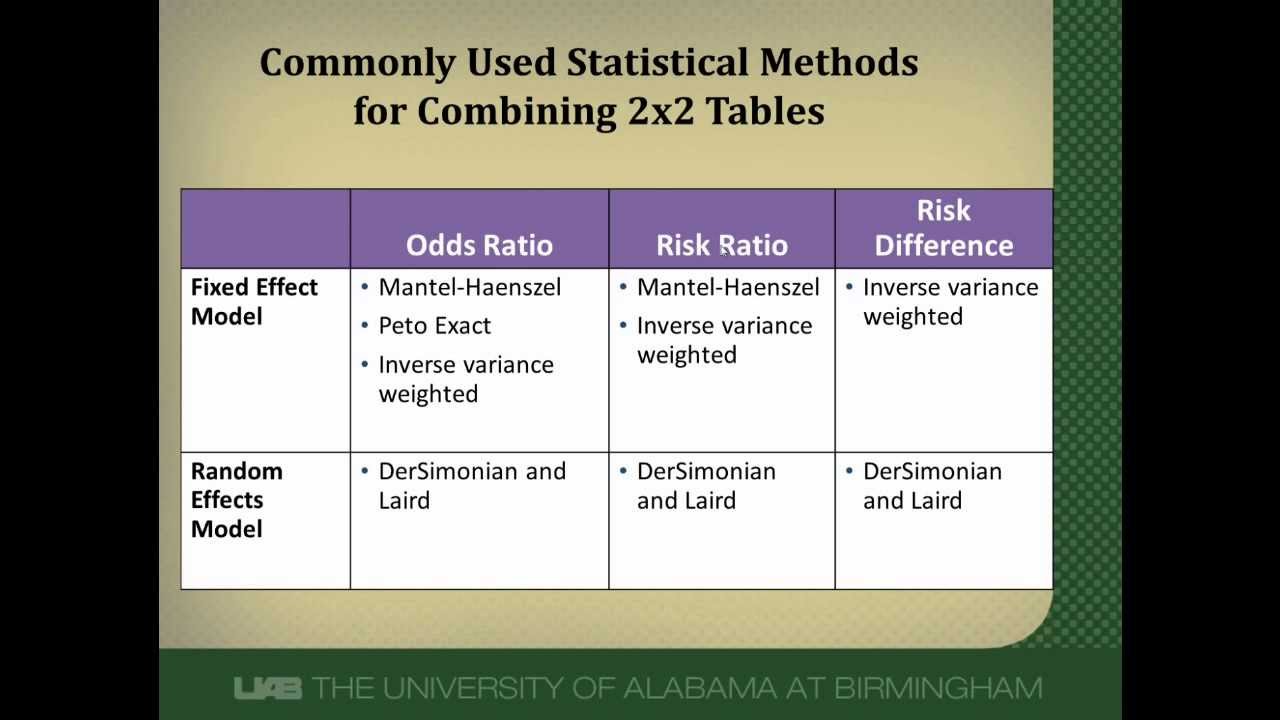
fixed effects, random effects, linear model, multilevel analysis, mixed model, population, dummy variables. Fixed and random effects In the specification of multilevel models, as discussed in [1] and [3], an important question is, which explanatory variables (also called independent variables or covariates) to give random effects.
Chapter 9 Random Effects Data Analysis in R
The analysis based on a random-effects model is shown in Figure 2. The effect size and confidence interval for each study appear on a separate row. The summary effect and its confidence interval are displayed at the bottom. Note that we have deliberately (if somewhat artificially) used the same data for the fixed-effect and random-effects.
PPT Fixed vs. Random Effects PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2615469
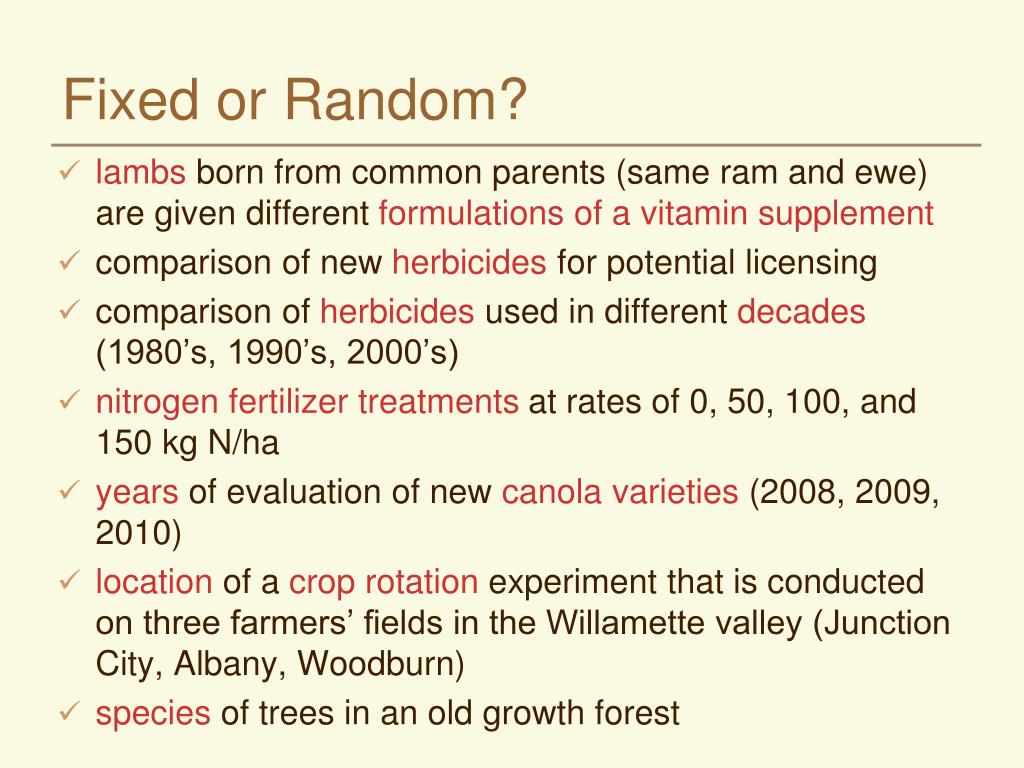
This paper assesses the options available to researchers analysing multilevel (including longitudinal) data, with the aim of supporting good methodological decision-making. Given the confusion in the literature about the key properties of fixed and random effects (FE and RE) models, we present these models' capabilities and limitations. We also discuss the within-between RE model, sometimes.